Free knowledge to monitor the world of events. Have a look at our must read Blogs on Pharma, Finance, HR, Health and Cross Industry.
Quality Risk Management (QRM) in Pharmaceutical Industry
2022-01-06
Quality Risk Management (QRM) is the process of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating recognized risks connected with medicines and healthcare goods. An excellent Quality Risk Management programme can be created to reduce risk to a manageable level and deliver high-quality products to protect citizens' health.
This research will demonstrate the principles of Quality Risk Management and its practical application in the pharmaceutical business, which will aid in the development and production of high-quality medicinal goods. Pharmaceutical companies have incorporated its concepts, tools, and processes in a variety of ways and at varying rates.
What is Risk?
The possibility of causing harm and the severity of that harm are combined to form risk. Personnel risks, product risks due to cross-contamination, and patient or public risks due to unpleasant drug side effects or contaminated drugs are all examples of risks. Product recalls posing a risk to the corporation, as does pollution, which poses a risk to the outside environment or atmosphere.

Identification of Risk
The below are some ideas for how to start or continue the process of risk identification :
- Using the worksheet to aid in the identification or prompting of risk.
- Past Records/Lessons
- Brainstorming
- Affinity diagrams
- Expert interviews
- Pre-Action Reviews
- Cause and effect diagram
- SWOT Analysis
Risk Identification and Management
Organizations must ensure that risk management plans do not introduce new or residual risk, and future outcomes must be evaluated and followed up on, with the breakthrough risk being analyzed to see how the process may be improved. Any severe or considerable risk must be managed, along with a contingency and fallback plan if necessary, to monitor and control risk. Metrics that provide insight into performance, trends and potential risk should be examined. Risk management activities should be conveyed to stakeholders.
The application of tactics or tricks to minimize the risk to an acceptable level is known as risk control. First and foremost, decide whether the risk is excessive. Decide how you'll manage the threats. New threats should not be created while the risk is being managed. It's possible that the deployment of risk-reduction measures will have an impact on the importance of other existing risks or create new ones. As a result, the risk assessment should be repeated to identify changes in risks as the risk reduction procedure is implemented.
Risk Communication
The interchange of risk information between decision management and others is known as risk communication. The outcomes of effective risk management should be tracked and shared. The nature of the risk, its severity, control, and other relevant information should all be shared.
Risk Review
Risk management is an ongoing process, and a framework should be put in place to review risks at regular intervals. The risks associated with the system's occurrences should be monitored at all times. The frequency with which risk management is reviewed is determined by the degree of the risk. It should be explicitly stated in the risk management document.
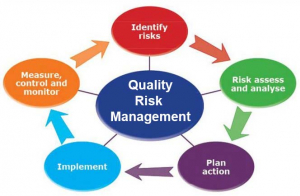
Benefits of Quality Risk Management (QRM)
Companies are able to meet regulatory obligations by implementing QRM. It's also a preventative approach that helps firms avoid being reactive by reducing risk. When more competent decision-making is in the planning stages, being prepared reduces ongoing risk and helps to minimize overall expenses. QRM also increases quality by increasing productivity and information exchange, with the potential to significantly minimize the amount of catch-up effort required to mitigate the effects of poor quality.
Prior risks that became problems are either addressed or recognized and analyzed in a predictive manner for the future in this interactive and ongoing process. Instead of focusing resources and time on low-risk activities, process events, or systems, QRM gives a reason for focusing resources and time on the things that are truly important. Risk management may help companies make better, more informed decisions, give regulators more confidence in a company's ability to deal with possible hazards, and influence the scope and level of direct regulatory monitoring.
Conclusion
Quality Risk Management (QRM) can help you reduce risk and keep it at a manageable level. Reviewing, identifying, monitoring, and planning responses to risk or threats are critical elements in implementing QRM, and each department has a unique role to play in risk management. Quality risk management is dynamic, and it must adapt as internal and external situations change. It should be examined on a regular basis and after any major incident or variation.
Check out our pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical device related masterclass here.
Also check our In-house Training for your customized pharma learnings.
By Fazmi Zakam, Junior SEO Executive, GLC Europe, Colombo Office, Sri Lanka.
Get a feel for our events

Training Program for CMC Leaders - EU edition
14th September 2026 - 09th April 2027
Rich with practical insights and real-world applications
learn more >>
Training Program for CMC Leaders - US edition
14th September 2026 - 09th April 2027
Rich with practical insights and real-world applications
learn more >>
PSMF - System Master File From A - Z MasterClass - US edition
17-19 March, 2026
PSMFs purpose, structure, and regulatory requirements
learn more >>